How Do Police Recruits Run For: Essential Training Techniques

Police recruits face tough physical tests to show they’re ready for the job. They need to meet running standards set by police academies. This training includes sprinting and endurance to build their heart health.
Police Academy Running Standards
Future police officers face tough running tests in the academy. These tests show their endurance, speed, and agility. They are key for the tough work of law enforcement.
Required Running Times and Distances
The 1.5-mile run is a big test. Recruits must finish it in under 14 minutes and 40 seconds. This test checks their heart health and ability to keep a steady pace.
Speed and Endurance Benchmarks
- Recruits also need to do well in short sprints, like the 300-meter dash. Times vary by age and gender.
- Endurance is tested with sit-ups and push-ups for 1 minute. Standards depend on age and sex.
Academy Track Requirements
Police academies use special tracks to check recruits’ fitness. These tracks include intervals, hill repeats, and obstacle courses. They mimic real-life situations to test agility, coordination, and stamina.
| Physical Fitness Test Component | Entrance Level Standard (15th Percentile) | Graduation Level Standard (30th Percentile) |
|---|---|---|
| 1.5-Mile Run | 12:51 minutes | 12:15 minutes |
| One-Minute Sit-ups | 38 repetitions | 42 repetitions |
| One-Minute Push-ups | 29 repetitions | 34 repetitions |
| 300-Meter Run | 62 seconds | 55 seconds |
Physical Fitness Test Components
Aspiring police officers face a tough physical fitness test. This test checks their strength, endurance, and readiness for law enforcement work. The police officer physical abilities test and law enforcement physical training include pushups, sit-ups, and running.
The West Covina Police Department has strict standards. Candidates must do at least 34 pushups in 1 minute, 38 sit-ups in 1 minute, run 1.5 miles in under 14:40, and complete a 300-meter run in under 65 seconds. These tests show if a person can meet the job’s physical demands.
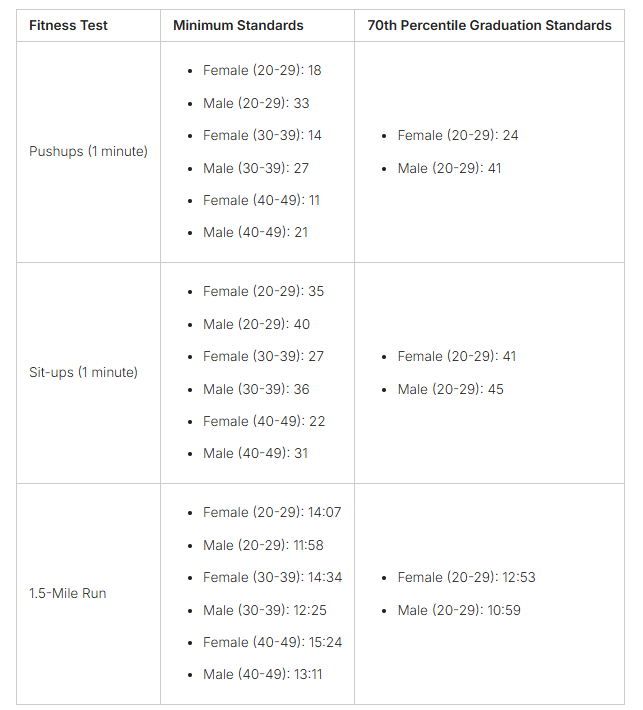
Candidates who pass these tests show they’re ready for police work. The tests make sure only the best physically are chosen for the job.
How Do Police Recruits Run For Academy Preparation
Getting ready for police academy is key for those wanting to join law enforcement. Running drills test recruits’ heart health. Those who train before the academy do better.
Pre-Academy Conditioning
Start a conditioning program a few months before the academy. It should include running to build endurance and strength training to boost running. Don’t forget flexibility exercises to avoid injuries.
Training Schedule Development
- Make a steady running plan, increasing distance and speed over time.
- Add interval, hill, and tempo runs to boost speed and stamina.
- Include rest days to avoid burnout and injury.
Running Equipment Essentials
Good running gear is vital for performance and comfort. Essential items are:
- Quality, fitting running shoes
- Breathable, moisture-wicking clothes
- A stopwatch or GPS for tracking
Some police departments have pre-academy programs. These help recruits get ready for the academy’s physical challenges. By focusing on running drills and heart health, future officers can succeed.
Sprint Training Requirements
Police recruits need sprint training for the academy. The 300-meter run is a big part of the test. It shows how fast and quick they need to be.
They start with short sprints and get longer and harder. These drills improve their power, quickness, and ability to act fast. Interval training adds to their police recruit sprint training and police academy running drills.
These workouts help recruits be fast and agile. They need this for chasing suspects or emergencies. The skills they learn are key for the police academy and their future jobs.
Distance Running Protocols
Police academy training includes a tough 1.5-mile run test. This test checks recruits’ endurance and heart health. They need to finish in under 14 minutes and 40 seconds. To pass, recruits must follow specific training plans.
1.5-Mile Run Standards
The 1.5-mile run is key in police recruit tests. It shows how well a person can handle hard physical tasks. It’s important for police training, showing they can keep up with demanding work.
Endurance Building Techniques
To get ready for the 1.5-mile run, recruits use different training methods. They focus on improving their heart health and running skills:
- They start with short runs and slowly increase the distance.
- They do long, slow runs to boost their heart health.
- They use interval training to get better at running fast and then resting.
Being consistent is vital in police training. By sticking to a plan and pushing themselves, recruits can get the stamina needed. This helps them do well in the 1.5-mile run and other tough police tasks.
Obstacle Course Running Challenges
Police academy training often includes obstacle course running. This simulates real-world scenarios officers might face. It tests their physical abilities and problem-solving skills.
The MoveStrong Obstacle Course has many challenges. These include Cargo Net Climb, Farmer Carry Logs, and Dual Rope Climb Station. These obstacles improve endurance, stamina, and strength. They also boost flexibility, agility, balance, and heart health.
Obstacle course training isn’t just for police academies. Events like the Spartan Race and Zombie Mud Run let civilians test their skills. These races have obstacles like wall climbs and mud pits.
The GORUCK Challenge is inspired by Special Forces training. It’s a 10-12 hour, 15-20 mile event that tests mental and physical endurance. The Civilian Military Combine (CMC) has a 5-mile race with 25 obstacles, including the “Flying Monkey” challenge from American Ninja Warrior.
Obstacle course training improves physical abilities and builds camaraderie. It teaches determination and a sense of accomplishment. Participants gain respect for the skills and dedication of police officers and public safety professionals.
Cardiovascular Training Methods
Police recruits need to get in shape for their duties. They should focus on heart rate zones and recovery. This helps them perform better in training and on the job.
Heart Rate Zones
Recruits should train in heart rate zones from 50% to 85% of their max. This boosts their aerobic capacity and endurance. It’s a safe way to improve without overdoing it.
Recovery Techniques
Recovery is key for recruits to stay fit. They should cool down, rest, and do light activities. This keeps them injury-free and performing well.
| Heart Rate Zone | Benefits | Recommended Duration |
|---|---|---|
| 50-60% of Max HR | Warm-up, active recovery | 10-15 minutes |
| 60-70% of Max HR | Aerobic endurance | 20-40 minutes |
| 70-80% of Max HR | Aerobic power | 10-20 minutes |
| 80-85% of Max HR | Anaerobic threshold | 5-10 minutes |
Police recruits can get in shape by using heart rate zones and recovery. This balanced training boosts their fitness for law enforcement. It’s all about police recruit cardiovascular fitness and law enforcement physical training.
Running Assessment Metrics
As police recruits get ready for law enforcement, their fitness is checked through running tests. These tests are key to seeing if they’re ready for police work.
The timed 1.5-mile run is a main test. It shows how well a recruit’s heart and lungs work. They also do a 300-meter sprint to test their quickness and strength.
There are more tests too. Police recruitment running requirements include checking heart rate recovery and VO2 max. These tests show how well a recruit’s heart and lungs work during exercise.
These tests aren’t just one time. Recruits keep getting checked as they train. They look at how fast they can run and how well they can keep going. This helps make sure police fitness test standards are met and recruits are ready for their jobs.
| Assessment Metric | Description | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| 1.5-Mile Run | Timed distance run | Evaluates cardiovascular endurance and overall running performance |
| 300-Meter Sprint | Timed short-distance run | Assesses explosive speed and power |
| Heart Rate Recovery | Measure of heart rate decline after exercise | Provides insights into cardiovascular health and fitness |
| VO2 Max Estimation | Measure of the body’s ability to utilize oxygen during exercise | Indicates aerobic fitness and endurance capacity |
Combined Strength and Running Workouts
Being a police officer requires top-notch physical fitness. Recruits need to mix strength training with running to succeed. Circuit training programs, which include bodyweight exercises, weightlifting, and running drills, help them get fit for the job.
Circuit Training Programs
Circuit training is a smart way to get fit for the police academy. It involves doing a series of exercises fast, with little rest. This method boosts strength, power, and heart health, preparing recruits for law enforcement’s many challenges.
Functional Fitness Integration
Police recruits should also work on functional fitness. This training focuses on movements that match real-life police tasks, like lifting or chasing suspects. It helps them become agile, coordinated, and ready for the field.
Injury Prevention Strategies
Keeping up with the physical demands of law enforcement is tough. Police recruits face a high risk of injuries during training. It’s important to have strategies to prevent injuries and keep recruits safe.
Strength training is a key strategy. Doing strength exercises 2-4 times a week can make the body stronger and less injury-prone. It’s important to learn the right techniques and start slowly to avoid risks.
Good posture and changing positions often can prevent muscle and joint problems. Drinking enough water and eating well also helps. These habits improve performance and aid in recovery.
Wearing the right shoes for long hours can prevent foot and ankle injuries. Recovery methods like foam rolling and stretching help too. Getting enough rest is also key to avoiding injuries.
Knowing about nutrition, sleep, and stress is important for staying healthy. Getting advice from health experts can help. They can offer tips on preventing injuries and recovering faster.
Mental health is just as important as physical health. Mindfulness and support can help with stress. A holistic approach to injury prevention helps recruits succeed in their training and future careers.
Running Performance Progression
Police recruits face tough training at the academy. Their running is closely watched and graded. The aim is to see them get better at running and staying fit over time.
Time Improvement Techniques
The academy uses different training methods to boost recruits’ running. Interval training mixes fast runs with rest. Hill runs build leg strength. Tempo runs keep a steady pace to improve heart health.
Performance Tracking Methods
The academy tracks recruits’ running with various methods. Timed runs, like the 1.5-mile run, show their progress. Recruits also track their own runs, including distance and heart rate. Some use fitness trackers for more detailed insights.
| Fitness Test Component | Hosting Agency (HA) Recruits | Participating Agency (PA) Recruits |
|---|---|---|
| Push-Ups (Repetitions) | Approximately 8% less than PA recruits | Approximately 8% more than HA recruits |
| Sit-Ups (Repetitions) | Approximately 12% less than PA recruits | Approximately 12% more than HA recruits |
The table shows the push-up and sit-up differences between HA and PA recruits. It shows the need for detailed fitness tests and training. This ensures recruits are ready for the police fitness test and police recruitment running requirements.
Conclusion
The journey of police recruits is filled with sprinting, endurance, and obstacle courses. They must meet tough running standards to succeed. This includes running 1.5 miles in under 14:40 and sprinting 300 meters in under 65 seconds.
Staying fit is vital for police work. This means regular training, good nutrition, and avoiding injuries. By improving speed, endurance, and heart health, recruits get ready for any situation. They also keep themselves and their communities safe.
Police officers must always be aware of their surroundings. This helps them stay safe and ready for anything. Programs like the Chicago Police Department’s training and the U.S. Department of Justice’s diversity program are key. They help build strong community ties and a diverse police force.






